History of Trading
The concept of trading is ancient, of course. It began with simple bartering, where early humans exchanged surplus goods—what they had for what they needed. This was the original and fundamental form of commerce.
Trade grew as civilisations did. The Silk Road and other great trade routes did more than just move goods; they also spread culture, knowledge, and new technologies across huge areas.
The creation of money and, later, formal stock exchanges changed the game. The Dutch East India Company and other companies that started in the 1600s came up with the idea of public shares and set the stage for today's financial markets.
That long history has brought us to today's electronic markets, which are instant. Now, trading happens all over the world on digital platforms, which is a long way from its simple bartering roots.
How Does Trading Work?
The first step is to open a demat account and trading account with a broker who is registered. This account is how you connect to the stock exchanges, which is where all the action is.
After that, you can use your broker's online platform to buy or sell certain stocks. The exchange then matches up all of these orders.
Your trade is complete—and a profit or loss is locked in—only when you close out that initial position by making an opposite trade.
Types of Trading in Stock Market
Trading isn't a one-size-fits-all activity. Different styles are defined by the timeframe traders operate in.
Scalping
Scalping is trading in its most intense form. Scalpers try to skim tiny profits from smaller price flickers, often making dozens or even hundreds of trades in a single day. Positions may last only seconds.
Because the individual gains are so small, volume is everything. The real danger is that a few bad trades can easily erase a day's worth of tiny wins, so a rock-solid exit plan is non-negotiable.
Frankly, this style demands machine-like focus and discipline. It's a high-stress game that is absolutely not meant for newcomers.
Day Trading
Day trading is a step back from the frenzy of scalping. You're still buying and selling stocks within a single day, but you might only make a handful of more deliberate trades that last for minutes or hours.
The golden rule is simple: all positions must be closed by the end of the day. This strategy avoids the risk of overnight news or events wrecking your trade before the market even opens.
It's a field that rewards a deep understanding of market volatility and technical charts, making it a playground for more experienced traders.
Swing Trading
This style is all about catching market "swings". You hold a stock for a few days or maybe a few weeks to profit from a single price move.
It’s a game of patterns. Swing traders live in the charts, using technical analysis to predict the market’s next likely direction.
Momentum Trading
Momentum trading is like jumping onto a moving train. You're looking for a stock that's already surging upward with strong momentum.
The belief here is simple: an object in motion—in this case, a stock's price—tends to stay in motion for a while.
Instead of hunting for bargains, you are actively looking for strength. The goal is to buy a stock that's already high, with the expectation of selling it even higher.
This isn't about long-term value; it's purely about riding the current wave of market enthusiasm and positive sentiment.
Knowing when to get off the train is critical. You're trying to sell right as that momentum peaks, just before the crowd starts to lose interest.
Because the percentage moves might be small, traders often use larger amounts of capital to make these trades meaningful.
A momentum trade can be a quick flip over a few hours or a ride that lasts for several days.
Position Trading
Position trading is a long game. Here, you're holding a position for weeks, months, or sometimes even longer than a year.
The whole idea is to capture the huge, major market trends and completely ignore all the distracting daily noise.
This requires real patience. Your decisions are guided by big-picture economic fundamentals, not by fleeting blips on a price chart.
Additional Read:- Types of trading in stock market
What is Online Trading in India?
Online trading can be easily done just by opening a Demat and Trading Account with any SEBI registered broker, which offers online services.
Opening an account can be done in a matter of just 10 minutes, all you need are the following documents- PAN card, address proof, AADHAAR card, a mobile number linked to AADHAAR, bank statement, canceled cheque leaf, and photograph.
In online trading, you can place your trade orders or cancel orders at your will and from the comforts of your home. You can also buy shares or invest in an IPO or buy Mutual Funds.
Online Trading vs Offline Trading:
Feature
| Online Trading
| Offline Trading
|
Convenience
| Accessible from anywhere with internet access
| Requires physical presence or phone calls to the broker
|
Speed
| Instant order execution and real-time market updates
| Slower execution due to manual processes
|
Cost
| Generally lower brokerage fees and transaction costs
| Higher brokerage fees and additional service charges
|
Information Access
| Immediate access to research, analytics, and market data
| Limited access to timely market information
|
Control
| Full control over trading decisions and portfolio management
| Relies on the broker for executing trades and managing the portfolio
|
Security
| Advanced encryption and secure trading platforms
| Security depends on the broker’s protocols and processes
|
Flexibility
| Wide range of trading tools and customizable platforms
| Limited flexibility and fewer trading tools available
|
What are the Advantages of Trading?
Below are some advantages of trading in the share market-
Take Advantage of the Growing Economy
When an economy grows, it also facilitates the growth of corporate earnings, this is because the economic growth creates more job opportunities, resulting in more income and more sales. Thus, an investor investing his/her money in the stock of the business, influenced by economic growth helps it to grow better.
Easy Process of Buying and Selling
Buying and selling of shares in the stock market is simple and easy for all investors, all you need is a Demat account which can be opened through a broker, financial planner, or online mode. Opening an account hardly takes 15 minutes to set up and start your investment journey. Once this is done, you can place your buy/sell orders.
Flexibility to Invest in a Smaller Amount
A new investor can even start with a small amount by purchasing stocks of small-cap or mid-cap companies but in smaller units.
Liquidity
Stocks are known as liquid assets as they can easily be converted into cash at any point in time. When compared to other financial assets.
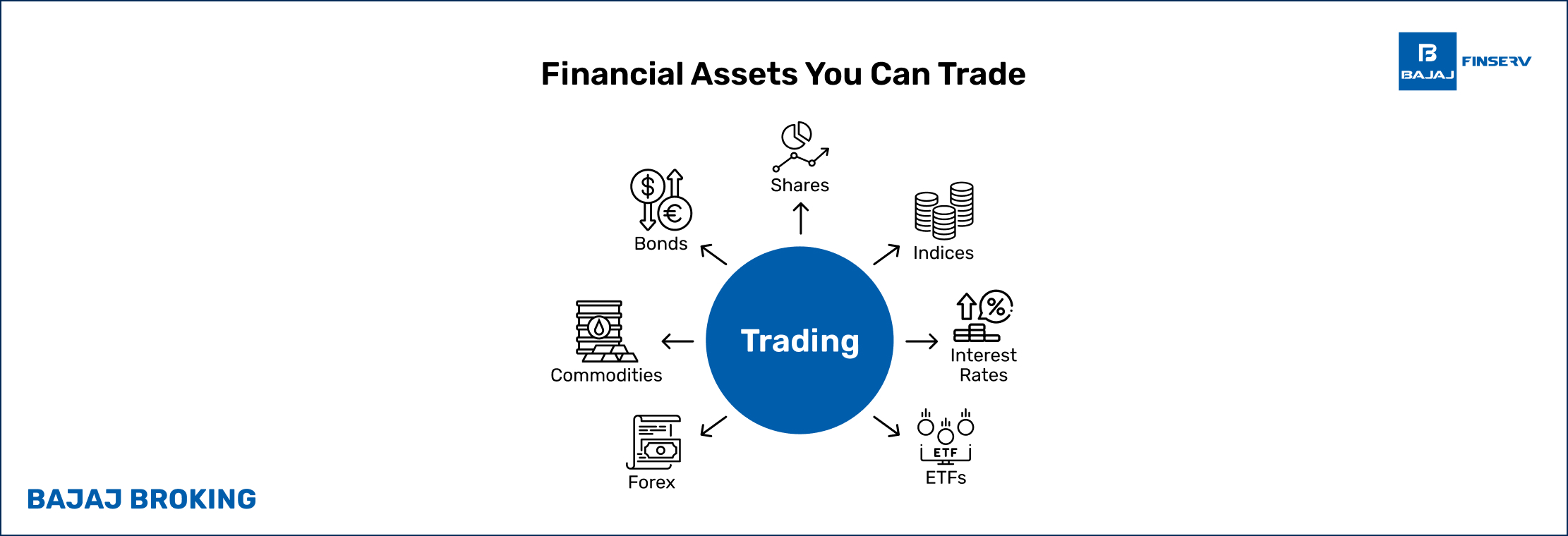
What Assets and Markets Can You Trade?
Various assets can be traded across multiple markets. These include stocks, which are traded on stock exchanges; bonds, traded in bond markets; commodities like gold, silver, and oil, traded on commodity exchanges; currencies, traded in the forex market; and derivatives like futures and options, traded on derivatives exchanges. Additionally, you can trade mutual funds, ETFs, and much more. Each market has its own set of rules, trading hours, and strategies, offering a range of opportunities to match different trading preferences and risk profiles.
Current Impact of Online Trading
Online platforms have completely changed the game. They've given everyday investors powerful tools and direct market access that was once the exclusive domain of professionals.
Trading vs Investing
When it comes to wealth creation, both trading and investing are two important attributes of it. For instance, you and your brother bought an equal amount of seeds and you sold them to someone on the same day because you could earn a profit. On the other hand, your brother sowed the seeds and let them grow for a year till they have new seeds. He sold the lot and continued to sow the new seeds and grow crops. By investing in his seeds, he too made profit however, took a different approach than you did.
Identity Proof: PAN Card
Address Proof: Either Aadhaar Card, Passport, Driving License, Voter id or last 3 months bank statement
Photograph
Signature on white paper
Bank Details: Any Bank proof (cheque or Passbook) bearing client name, account number & IFSC code
Income Proof: Either 6 months bank statement, 3 months’ salary slip, net-worth certificate, Holding Report, ITR Statement or Demat Holding Statement.
Advantages of Opening a Trading Account
Trading Accounts offer manifold benefits to the investors, making the share trading ecosystem more robust and efficient. A few of such advantages are detailed below:
This is the difference between both trading and investing in simple terms.
Let’s study below trading vs investing:
Period
In trading, stocks are usually held by the investor for a short period (for a week or a day), whereas investing is an approach that works on the buy and hold principle, and the investor may invest for several years as well.
Capital growth
In trading, traders look at the price movements of stocks, and if they notice an increase in price, they sell the stock to book profits. Whereas in investing, it requires a patient approach. Wealth is created by compounding interest over the years.
Risk
Both trading and investing imply risks. Trading comparatively involves higher risks as the price might go high or low in a short interval. On the other hand, investing is an art, it takes a while to develop. Therefore, it involves lower risk.
Final Thoughts
In the end, whether you're trading or investing, making smart decisions is what matters. I think building a real, fundamental understanding of how the market works is the only reliable way to manage risk effectively.
Additional Read: What is Trading Account